Hybrid vehicle drivetrain

Hybrid vehicle drivetrains transmit power to the driving wheels for hybrid vehicles. A hybrid vehicle has multiple forms of motive power.
Hybrids come in many configurations. For example, a hybrid may receive its energy by burning petroleum, but switch between an electric motor and a combustion engine.
Electrical vehicles have a long history combining internal combustion and electrical transmission –as in a diesel-electric powertrain–, although they have mostly been used for rail locomotives. A diesel-electric powertrain fails the definition of hybrid because the electrical drive transmission directly replaces the mechanical transmission rather than being a supplementary source of motive power. One of the earliest forms of hybrid land vehicle is the ‘trackless’ trolleybus of the 1930s, which normally used traction current delivered by wire. The trolleybus was commonly fitted with an internal combustion engine (ICE) either to directly power the bus or to independently generate electricity. This enabled the vehicle to manoeuvre around obstacles and broken overhead transmission wires.
The powertrain includes all of the components used to transform stored potential energy. Powertrains may either use chemical, solar, nuclear or kinetic and make them useful for propulsion. The oldest example is the galley that used sails and oars. A common modern example is the electric bicycle. Hybrid electric vehicles combine a battery or supercapacitor supplemented by an ICE that can recharge the batteries or power the vehicle. Other hybrid powertrains use flywheels to store energy.
Among the different types of hybrid vehicles, only the electric/ICE type was commercially available as of 2016. One variety operated in parallel to simultaneously provide power from both motors. Another operated in series with one source exclusively providing the power and the second providing electricity. Either source may provide the primary motive force, with the other augmenting the primary.
Other combinations offer efficiency gains from superior energy management and regeneration that are offset by expense, complexity and the battery limitations. Combustion-electric (CE) hybrids have battery packs with far larger capacity than a combustion-only vehicle. A combustion-electric hybrid has batteries that are light that offer higher energy density that are far more costly. ICEs require only a battery large enough to operate the electrical system and ignite the engine.
Types by design
Parallel hybrid
Parallel hybrid systems have both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor that can both individually drive the car or both coupled up jointly giving drive. This is the most common hybrid system as of 2016.
If they are joined at an axis (in parallel), the speeds at this axis must be identical and the supplied torques add together. (Most electric bicycles are of this type.) When only one of the two sources is in use, the other must either also rotate (idle), be connected by a one-way clutch or freewheel.
With cars the two sources may be applied to the same shaft (for example with the electric motor connected between the engine and transmission), turning at equal speeds and the torques adding up with the electric motor adding or subtracting torque to the system as necessary. (The Honda Insight uses this system.)
Parallel hybrids can be further categorized by the balance between the different motors are at providing motive power: the ICE may be dominant (engaging the electric motor only in specific circumstances) or vice versa; while in others can run on the electric system alone but because current parallel hybrids are unable to provide electric-only or internal combustion-only modes they are often categorized as mild hybrids (see below).
Parallel hybrids rely more on regenerative braking and the ICE can also act as a generator for supplemental recharging. This makes them more efficient in urban ‘stop-and-go’ conditions. They use a smaller battery pack than other hybrids. Honda’s Insight, Civic, and Accord hybrids are examples of production parallel hybrids. General Motors Parallel Hybrid Truck (PHT) and BAS Hybrids such as the Saturn VUE and Aura Greenline and Chevrolet Malibu hybrids also employ a parallel hybrid architecture.
Through The Road (TTR) Hybrid
An alternative parallel hybrid is the ‘through the road’ type. In this system a conventional drivetrain powers one axle, with an electric motor or motors driving another. This arrangement was used by the earliest ‘off track’ trolleybuses. It in effect provides a complete backup power train. In modern motors batteries can be recharged through regenerative braking or by loading the electrically driven wheels during cruise. This allows a simpler approach to power-management. This layout also has the advantage of providing four-wheel-drive in some conditions. (An example of this principle is a bicycle fitted with a front hub motor, which assists the cyclist’s pedal power at the rear wheel.) Vehicles of this type include the Audi 100 Duo II, Subaru VIZIV and Peugeot 307 Hybrid HDi concept cars, the PSA Group vehicles Peugeot 3008, Peugeot 508, 508 RXH, Citroen DS5 all using the HYbrid4 system, the Volvo V60 plug-in hybrid, the BMW 2 Series Active Tourer, BMW i8, and the second generation Honda NSX.
Series hybrid
Series hybrids are also referred to as extended-range electric vehicles (EREV) or range-extended electric vehicles (REEV). (Series hybrids with particular characteristics are classified as range-extended battery-electric vehicle (BEVx) by the California Air Resources Board.)
Electric transmission has been available as an alternative to conventional mechanical transmissions since 1903. Typically mechanical transmissions impose many penalties, including weight, bulk, noise, cost, complexity and a drain on engine power with every gear-change, whether accomplished manually or automatically. Unlike ICEs, electric motors do not require a transmission.
In effect the entire mechanical transmission between the ICE and the wheels is removed and replaced by an electric generator, some cable and controls, and electric traction motors, with the benefit that the ICE is no longer directly connected to the demand.
This is a series-hybrid arrangement and is common in diesel-electric locomotives and ships (the Russian river ship Vandal, launched in 1903, was the world’s first diesel-powered and diesel-electric powered vessel) and Ferdinand Porsche successfully used this arrangement in the early 20th century in racing cars, including the Lohner-Porsche Mixte Hybrid. Porsche named the system System Mixte, which had a wheel hub motor arrangement, with a motor in each of the two front wheels, setting speed records.
The arguments of greater flexibility, higher efficiency and less emissions at the point of use are achieved in a series-hybrid system for road vehicles when an intermediate electric battery, acting as an energy buffer, sits between the electric generator and the electric traction motors.
The ICE turns a generator and is not mechanically connected to the driving wheels. This isolates the engine from demand, allowing it to consistently operate at its most efficient speed. Since the primary motive power is generated by the battery, a smaller generator/engine can be fitted as compared to a conventional direct drive engine. Electric traction motors can receive electricity from the battery, or directly from the engine/generator or both. Traction motors frequently are powered only by the electric battery, which can be charged from external sources such as the electricity grid.
This allows a vehicle with an engine/generator that only operates when needed, such as when the battery is depleted, or to charge the batteries.
Electric traction motors
Electric motors are more efficient than ICEs, with high power-to-weight ratios providing torque over a wide speed range. ICEs are most efficient when turning at a constant speed.
ICEs can run optimally when turning a generator. Series-hybrid systems offer smoother acceleration by avoiding gear changes. Series-hybrids incorporate:
Electric traction only – using only electric motors to turn the wheels.
ICE – turns only a generator.
Generator – turned by the ICE to generate electricity and start the engine.
Battery – energy buffer.
Regenerative braking – The drive motor becomes a generator and recovers energy by converting kinetic to electrical energy, also slowing the vehicle and preventing thermal losses.
In addition:
May be plugged into the grid to recharge the battery.
Supercapacitors assist the battery and recover most energy from braking.
In detail
The electric motor may be entirely fed by electricity from the battery or via the generator turned by the ICE, or both. Such a vehicle conceptually resembles a diesel-electric locomotive with the addition of a battery that may power the vehicle without running the ICE and acting as an energy buffer that is used to accelerate and achieve greater speed; the generator may simultaneously charge the battery and power the electric motor that moves the vehicle.
When the vehicle is stopped the ICE is switched off without idling, while the battery provides whatever power is needed at rest. Vehicles at traffic lights, or in slow moving stop-start traffic need not burn fuel when stationary or moving slowly, reducing emissions.
Series-hybrids can be fitted with a supercapacitor or a flywheel to store regenerative braking energy, which can improve efficiency by recovering energy otherwise lost as heat through the braking system. Because a series-hybrid has no mechanical link between the ICE and the wheels, the engine can run at a constant and efficient rate regardless of vehicle speed, achieving higher efficiency (37%, rather than the ICE average of 20%) and at low or mixed speeds this could result in ~50% increase in overall efficiency (19% vs 29%).
Lotus offered an engine/generator set design that runs at two speeds, giving 15 kW of electrical power at 1,500 rpm and 35 kW at 3,500 rpm via the integrated electrical generator, used in the Nissan concept Infiniti Emerg-e.
This operating profile allows greater scope for alternative engine designs, such as a microturbine, rotary Atkinson cycle engine or linear combustion engine.
The ICE is matched to the electric engine by comparing the output rates at cruising speed. Generally, output rates for combustion engines are provided for instantaneous (peak) output rates, but in practice these can’t be used.)
The use of an electric motor driving a wheel directly eliminates the conventional mechanical transmission elements: gearbox, transmission shafts and differential, and can sometimes eliminate flexible couplings.
In 1997, Toyota released the first series-hybrid bus sold in Japan. Designline International of Ashburton, New Zealand produces city buses with a microturbine powered series-hybrid system. Wrightbus produces series hybrid buses including the Gemini 2 and New Routemaster. Supercapacitors combined with a lithium ion battery bank have been used by AFS Trinity in a converted Saturn Vue SUV vehicle. Using supercapacitors they claim up to 150 mpg in a series-hybrid arrangement.
Well known automotive series hybrid models include the variant of the BMW i3 that is equipped with a range extender. Another example of a series hybrid automobile is the Fisker Karma. The Chevrolet Volt is almost a series hybrid, but also includes a mechanical link from the engine to the wheels above 70 mph.
Series-hybrids have been taken up by the aircraft industry. The DA36 E-Star, an aircraft designed by Siemens, Diamond Aircraft and EADS, employs a series hybrid powertrain with the propeller turned by a Siemens 70 kW (94 hp) electric motor. A power sapping propeller speed reduction unit is eliminated. The aim is to reduce fuel consumption and emissions by up to 25 percent. An onboard 40 hp (30 kW) Austro Engine Wankel rotary engine and generator provides the electricity.
The Wankel was chosen because of its small size, low weight and great power to weight ratio. (Wankel engines also run efficiently at a constant speed of approximately 2,000 RPM which is suited to generator operation. Keeping to a constant/narrow band offsets many of the perceived disadvantages of the Wankel engine in automotive applications.)
The electric propeller motor uses electricity stored in batteries, with the engines not operating, to take off and climb reducing sound emissions. The powertrain reduces the weight of the plane by 100 kilos relative to its predecessor. The DA36 E-Star first flew in June 2013, making this the first ever flight of a series hybrid powertrain. Diamond Aircraft state that the technology is scalable to a 100-seat aircraft.
In-wheel motors
If the motors are attached to the vehicle body, flexible couplings are required but not if the traction motors are integrated into the wheels. One disadvantage is that the unsprung mass increases and suspension responsiveness decreases, which impacts ride and potentially safety. However the impact should be minimal as electric motors in wheel hubs such as Hi-Pa Drive, may be very small and light having exceptionally high power-to-weight ratios and braking mechanisms can be lighter as the wheel motors brake the vehicle.
Advantages of individual wheel motors include simplified traction control, all wheel drive if required and a lower floor (useful for buses and other specialised vehicles (some 8×8 all-wheel drive military vehicles use individual wheel motors). Diesel-electric locomotives have used this concept (individual motors driving axles of each pair of wheels) for 70 years.[full citation needed]
Other measures include lightweight aluminium wheels to reduce the unsprung mass of the wheel assembly; vehicle designs may be optimized to lower the centre of gravity by locating heavier elements (including battery) at floor level; In a typical road vehicle the power-transmission setup may be smaller and lighter than the equivalent conventional mechanical power-transmission setup, liberating space; the combustion generator set only requires cables to the driving electric motors, increasing flexibility in major component layout spread across a vehicle giving superior weight distribution and maximizing vehicle cabin space and opening up the possibility of superior vehicle designs exploiting this flexibility.
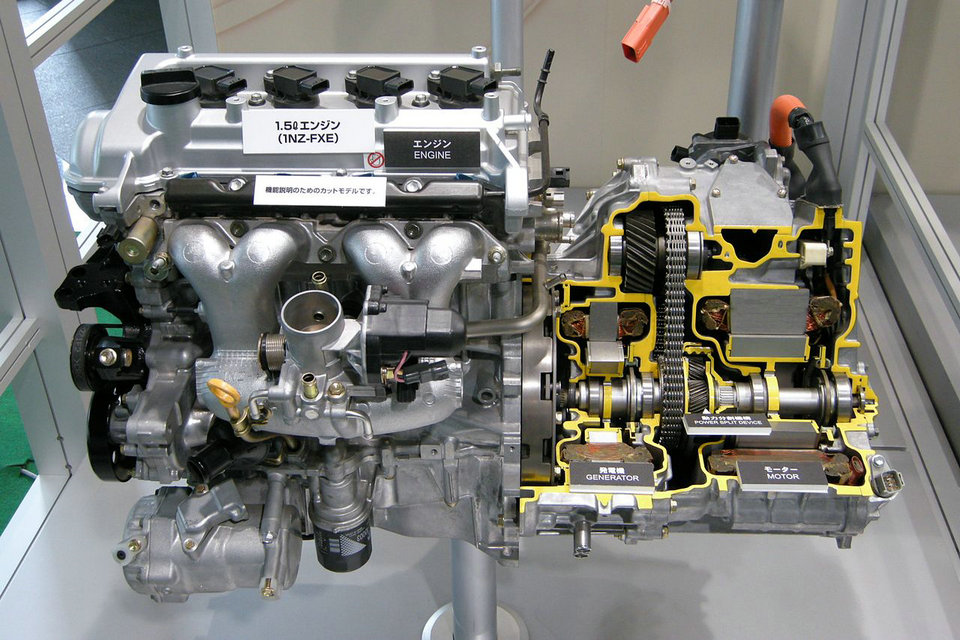
Power-split or series-parallel hybrid
Power-split hybrid or series-parallel hybrid are parallel hybrids that incorporate power-split devices, allowing for power paths from the ICE to the wheels that can be either mechanical or electrical. The main principle is to decouple the power supplied by the primary source from the power demanded by the driver.
ICE torque output is minimal at lower RPMs and conventional vehicles increase engine size to meet market requirements for acceptable initial acceleration. The larger engine has more power than needed for cruising. Electric motors produce full torque at standstill and are well-suited to complement ICE torque deficiency at low RPMs. In a power-split hybrid, a smaller, less flexible, and more efficient engine can be used. The conventional Otto cycle (higher power density, more low-RPM torque, lower fuel efficiency) is often modified to an Atkinson cycle or Miller cycle (lower power density, less low-rpm torque, higher fuel efficiency; sometimes called an Atkinson-Miller cycle). The smaller engine, using a more efficient cycle and often operating in the favorable region of the brake specific fuel consumption map, significantly contributes to the higher overall efficiency of the vehicle.
Interesting variations of the simple design (pictured at right) found, for example, in the well-known Toyota Prius are the:
fixed gear second planetary gearset as used in the Lexus RX400h and Toyota Highlander Hybrid. This allows for a motor with less torque but higher power (and higher maximum rotary speed), i.e. higher power density
Ravigneaux-type planetary gear (planetary gear with 4 shafts instead of 3) and two clutches as used in the Lexus GS450h. By switching the clutches, the gear ratio from MG2 (the traction motor) to the wheel shaft is switched, either for higher torque or higher speed (up to 250 km/h / 155 mph) while sustaining better transmission efficiency. This is effectively accomplished in the Generation 3 Prius HSDs (Prius v, Prius Plug-in and Prius c), although the Generation 3 HSD has this second planetary gear set fixed at 2.5:1, rather than switching between 1:1 and 2.5:1 as the “carrier” is held fixed.
Two additional planetary gear sets in combination with four clutches to create a Two-Mode Hybrid configuration able to operate in all-electric, blended electric and ICE, or ICE alone with four fixed gears. Examples of Two-Mode Hybrids include the General Motors Two-Mode Hybrid full-size trucks and SUVs, the BMW X6 ActiveHybrid and the Mercedes ML 450 hybrid.
Types by degree of hybridization
| Type | Start-stop system | Regenerative braking Electric boost | Charge-depleting mode | Rechargeable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micro hybrid | Yes | No | No | No |
| Mild hybrid | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Full hybrid | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Plug-in hybrid | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Micro hybrids
Micro hybrid is a general term given to vehicles that use some type of start-stop system to automatically shut off the engine when idling. Strictly speaking, micro hybrids are not real hybrid vehicles, because they do not rely on two different sources of power.
Mild hybrids
Mild hybrids are essentially conventional vehicles with some hybrid hardware, but with limited hybrid features. Typically, they are a parallel hybrid with start-stop only or possibly with modest levels of engine assist or regenerative braking. Mild hybrids generally cannot provide all-electric propulsion.
Mild hybrids like the General Motors 2004-07 Parallel Hybrid Truck (PHT) and the Honda Eco-Assist hybrids are equipped with a three-phase electric motor mounted within the bell-housing between the engine and transmission, allowing the engine to be turned off whenever the truck is coasting, braking, or stopped, yet restart quickly to provide power. Accessories can continue to run on electrical power while the engine is off, and as in other hybrid designs, regenerative braking recaptures energy. The large electric motor spins up the engine to operating speeds before injecting fuel.
The 2004–07 Chevrolet Silverado PHT was a full-size pickup truck. Chevrolet was able to get a 10% efficiency improvement by shutting down and restarting the engine on demand and using regenerative braking. The electrical energy was used only to drive accessories such as power steering. The GM PHT used a 42 volt system via three 12 volt vented lead acid batteries connected in series (36V total) to supply the power needed for the startup motor, as well as to power the electronic accessories.
General Motors then introduced their BAS Hybrid system, another mild hybrid implementation officially released on the 2007 Saturn Vue Green Line. Its “start-stop” functionality operates similarly to the Silverado, although via a belted connection to the motor/generator unit. However the GM BAS Hybrid System can also provide modest assist under acceleration and during steady driving, and captures energy during regenerative (blended) braking. BAS Hybrid offered as much as a 27% improvement in combined fuel efficiency in EPA testing of the 2009 Saturn VUE. The system can also be found on the 2008-09 Saturn Aura and the 2008-2010 Chevrolet Malibu hybrids.
Another way to offer start/stop is by employing a static start engine. Such an engine requires no starter motor, but employs sensors to determine the exact position of each piston, then precisely timing the injection and ignition of fuel to turn over the engine.
Mild hybrids are sometimes called Power assist hybrids as they use the ICE for primary power, with a torque-boosting electric motor connected to a (largely) conventional power train. The electric motor is mounted between the engine and transmission. It is essentially a large starter motor that operates when the engine needs to be turned over and when the driver “steps on the gas” and requires extra power. The electric motor may also restart the combustion engine and shutting down the main engine at idle, while the enhanced battery system is used to power accessories.
Ford has dubbed Honda’s hybrids “mild” in their advertising for the Escape Hybrid, arguing that the Escape’s full hybrid design is more efficient.
Full hybrids
A full hybrid, sometimes also called a strong hybrid, is a vehicle that can run on just the engine, the batteries, or a combination. The Toyota Prius, Toyota Camry Hybrid, Ford Escape Hybrid/Mercury Mariner Hybrid, Ford Fusion Hybrid/Lincoln MKZ Hybrid/Mercury Milan Hybrid, Ford C-Max Hybrid, Kia Optima Hybrid, as well as the General Motors 2-mode hybrid trucks and SUVs, are examples of this type of hybridization as they can operate on battery power alone. A large, high-capacity battery provides battery-only operation. These vehicles have a split power path that allows more flexibility in the drivetrain by inter-converting mechanical and electrical power. To balance the forces from each portion, the vehicles use a differential-style linkage between the engine and motor connected to the head end of the transmission.
The Toyota brand name for this technology is Hybrid Synergy Drive, which is used in the Prius, the Highlander Hybrid SUV and the Camry Hybrid. A computer oversees system operation, determining how to mix the power sources. The Prius operations can be divided into six distinct regimes.
Electric vehicle mode—The ICE is off and the battery powers the motor (or charges during regenerative braking). Used for idling when the battery state of charge (SOC) is high.
Cruise mode—The vehicle is cruising (i.e. not accelerating), and the ICE can meet the demand. The power from the engine is split between the mechanical path and the generator. The battery also powers the motor, whose power is summed mechanically with the engine. If the battery state-of-charge is low, part of the power from the generator charges the battery.
Overdrive mode—A portion of the rotational energy produces electricity, because the ICE’s full power is not needed to maintain speed. This electrical energy is used to drive the sun gear in the direction opposite its usual rotation. The end result has the ring gear rotating faster than the engine, albeit at lower torque.
Battery charge mode—Also used for idling, except that in this case the battery state-of-charge is low and requires charging, which is provided by the engine and generator.
Power boost mode—Employed in situations where the engine cannot maintain the desired speed. The battery powers the motor to complement the engine power.
Negative split mode—The vehicle is cruising and the battery state-of-charge is high. The battery provides power to both the motor (to provide mechanical power) and to the generator. The generator converts this to mechanical energy that it directs towards the engine shaft, slowing it down (although not altering its torque output). The purpose of this engine “lugging” is to increase the fuel economy of the vehicle.
Plug-in hybrid
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) has two defining characteristics. It:
Can be plugged into an electrical outlet to be charged.
Can travel powered only by the battery.
They are full hybrids, able to run on battery power. They offer greater battery capacity and the ability to recharge from the grid. They can be either parallel or series designs. They are also called gas-optional, or griddable hybrids. Their main benefit is that they can be gasoline-independent for significant distances, with the extended range of an ICE for longer trips. Electric Power Research Institute research found a lower total cost of ownership for PHEVs due to reduced service costs and gradually improving battery technology. The “well-to-wheel” efficiency and emissions of PHEVs compared to gasoline hybrids depends on the grid energy sources (the US grid is 30% coal; California’s grid is primarily natural gas, hydroelectric power, and wind power).
Prototypes of PHEVs, with larger battery packs that can be recharged from the power grid, were built in the U.S., notably at Andy Frank’s Hybrid Center at University of California, Davis. One production PHEV, the Renault Kangoo, went on sale in France in 2003. DaimlerChrysler built PHEVs based on the Mercedes-Benz Sprinter van. Light Trucks are offered by Micro-Vett SPA the so-called Daily Bimodale.
Types by power source
Electric-internal combustion engine hybrid
There are many ways to create an electric-Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) hybrid. The variety of electric-ICE designs can be differentiated by how the electric and combustion portions of the powertrain connect, at what times each portion is in operation, and what percent of the power is provided by each hybrid component. Two major categories are series hybrids and parallel hybrids, though parallel designs are most common today.
Most hybrids, no matter the specific type, use regenerative braking to recover energy when slowing down the vehicle. This simply involves driving a motor so it acts as a generator.
Many designs also shut off the internal combustion engine when it is not needed in order to save energy. That concept is not unique to hybrids; Subaru pioneered this feature in the early 1980s, and the Volkswagen Lupo 3L is one example of a conventional vehicle that shuts off its engine when at a stop. Some provision must be made, however, for accessories such as air conditioning which are normally driven by the engine. Furthermore, the lubrication systems of internal combustion engines are inherently least effective immediately after the engine starts; since it is upon startup that the majority of engine wear occurs, the frequent starting and stopping of such systems reduce the lifespan of the engine considerably.[dubious – discuss] Also, start and stop cycles may reduce the engine’s ability to operate at its optimum temperature, thus reducing the engine’s efficiency.
Electric-fuel cell hybrid
Fuel cell vehicles are often fitted with a battery or supercapacitor to deliver peak acceleration power and to reduce the size and power constraints on the fuel cell (and thus its cost); this is effectively also a series hybrid configuration.
Internal combustion engine-hydraulic hybrid
A hydraulic hybrid vehicle uses hydraulic and mechanical components instead of electrical. A variable displacement pump replaces the electric motor/generator. A hydraulic accumulator stores energy. The vessel typically carries a flexible bladder of pre-charged pressurized nitrogen gas. Pumped hydraulic fluid is compressed against the bladder storing the energy in the compressed nitrogen gas. Some versions have a piston in a cylinder rather than a pressurized bladder. The hydraulic accumulator is potentially cheaper and more durable than batteries. Hydraulic hybrid technology was originally implemented in Germany in the 1930s. Volvo Flygmotor used petro-hydraulic hybrids experimentally in buses from the early 1980s.
The initial concept involved a giant flywheel (see Gyrobus) for storage connected to a hydrostatic transmission. The system is under development by Eaton and several other companies, primarily in heavy vehicles like buses, trucks and military vehicles. An example is the Ford F-350 Mighty Tonka concept truck shown in 2002. It features an Eaton system that can accelerate the truck to highway speeds.
The system components were expensive, which precluded installation in smaller trucks and cars. A drawback was that the power motors were not efficient enough at part load. Focus switched to smaller vehicles. A British company made a breakthrough by introducing an electronically controlled hydraulic motor/pump that is efficient at all ranges and loads, making small applications of petro-hydraulic hybrids feasible. The company converted a BMW car to prove viability. The BMW 530i gave double the MPG in city driving compared to the standard car. The test used the standard 3,000 cc engine. Petro-hydraulic hybrids allows downsizing an engine to average power usage, not peak power usage. Peak power is provided by the energy stored in the accumulator.
The kinetic braking energy recovery rate is higher and therefore the system is more efficient than 2013-era battery charged hybrids, demonstrating a 60% to 70% increase in economy in EPA testing. In EPA tests a hydraulic hybrid Ford Expedition returned 32 mpg‑US (7.4 L/100 km) in urban driving and 22 mpg‑US (11 L/100 km) on the highway.
One research company’s goal was to create a fresh design to improve the packaging of gasoline-hydraulic hybrid components. All bulky hydraulic components were integrated into the chassis. One design claimed to reach 130mpg in tests by using a large hydraulic accumulator that is also the structural chassis. The hydraulic driving motors are incorporated within the wheel hubs and reversing to recover braking energy. The aim is 170 mpg in average driving conditions. Energy created by shock absorbers and kinetic braking energy that normally would be wasted assists in charging the accumulator. An ICE sized for average power use charges the accumulator. The accumulator is sized to run the car for 15 minutes when fully charged.
Internal combustion engine-pneumatic
Compressed air can power a hybrid car with a gasoline compressor to provide the power. Motor Development International in France was developing such air-powered cars. A team led by Tsu-Chin Tsao, a UCLA mechanical and aerospace engineering professor, collaborated with engineers from Ford to get pneumatic hybrid technology up and running. The system is similar to that of a hybrid-electric vehicle in that braking energy is harnessed and stored to assist the engine as needed during acceleration.
Human power-environmental power
Many land and water vehicles use human power combined with a further power source. Common are parallel hybrids, e.g. a sailboat with oars, motorized bicycles or a human-electric hybrid vehicle such as the Twike. Some series hybrids exist. Such vehicles can be tribrid vehicles, combining three power sources e.g. on-board solar cells, grid-charged batteries and pedals.
Aftermarket options
Conmarket/aftermarket powertrain can be added to a vehicle.
The conmarket solution is used when the user delivers glider (rolling chassis) and the hybrid (two engines) or all-electric (only an electric motor) powertrain kit to the automaker and receives the vehicle with the tech installed. An (electric or hybrid) powertrain can be added to a glider by an aftermarket installer.
In 2013 a University of Central Florida design team, On the Green, worked to develop a bolt-on hybrid conversion kit to transform an older model vehicle into a gas-electric hybrid.
A conversion of a 1966 Mustang was demonstrated by an engineer in California. The system replaced the alternator with a 12 kW (30 kW peak) brushless electric motor. Gas mileage and power improved.
Source from Wikipedia